- AustraliaEnglish
- BelgiumDutchFrench
- BrasilPortuguese
- CanadaEnglish
- FranceFrench
- GermanyGerman
- GlobalEnglishFrenchSpanish
- GreeceGreek
- IndiaEnglish
- ItalyItalian
- JapanJapanese
- LuxembourgFrench
- MexicoSpanish
- Middle East & AfricaEnglish
- NetherlandsDutch
- PolandPolish
- PortugalPortuguese
- SpainSpanish
- South AmericaSpanish
- SwedenSwedish
- TurkeyEnglish
- United KingdomEnglish
- United States of AmericaEnglish
PV and solar inverters explained
Solar inverters are essential components of PV systems. They convert the direct current (DC) generated by PV modules into alternating current (AC). SMA PV inverters are compatible with the PV modules of leading manufacturers. We also supply the right inverter for every area of application, be it a home, business or industry. Learn more about our innovative technology here.

SMA PV inverters
SMA Home & Commercial Energy Solution
String inverters
Sunny Boy 3-6 3 kW / 3.6 kW / 4 kW / 5 kW / 6 kW
Single-phase solar inverter for single-family homes.
Sunny Boy Smart Energy 3.6 kW / 4 kW / 5 kW / 6 kW
Our single-phase hybrid inverter for homes.
Sunny Tripower 3-6 3 kW / 4 kW / 5 kW / 6 kW
Three-phase solar inverter for private households.
Sunny Tripower 8-10 8 kW / 10 kW
Maximum yield for household systems and small commercial applications.
Sunny Tripower Smart Energy 5 kW / 6 kW/ 8 kW / 10 kW
Three-phase hybrid inverter for up to 100% self-sufficiency at home.
Sunny Tripower X 12 kW / 15 kW / 20 kW / 25 kW
Energy generation and management for larger households and commercial PV systems
Sunny Tripower CORE1 50 kW
Free-standing solar inverter for planning decentralized commercial PV systems.
Sunny Tripower CORE2 110 kW
Solar inverter for flexible planning of commercial rooftop and ground-mounted systems.
Sunny Highpower PEAK3 100 kW / 150 kW / 172 kW / 180 kW
For commercial systems: this solar inverter combines powerful components for the digital energy world of the future.
SMA Large Scale Energy Solutions
Central inverters
What is a PV inverter?
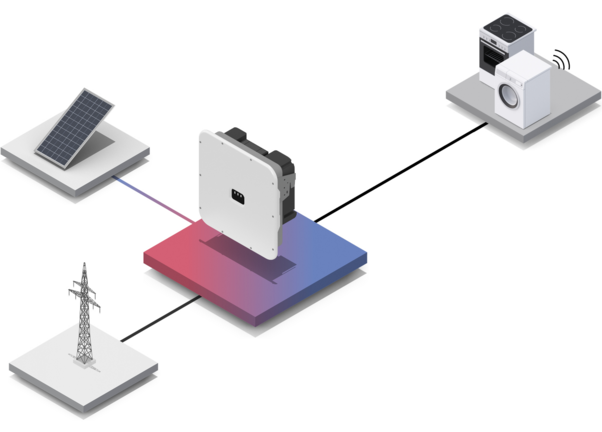
Solar Inverter – Definition: Every PV system requires at least one inverter. While the utility grid supplies alternating current (AC) and most domestic appliances and machines also run on alternating current, the PV modules on your roof generate direct current (DC). So, this first has to be converted into alternating current (AC) for everyday use. Otherwise you won't be able to use the energy you produce yourself or feed it into the utility grid.
How do solar inverters work?
Inverters are often described as the "heart" of a PV system because they play a central role in converting the direct current generated into usable alternating current. Without an inverter, efficient and reliable use of the solar power generated by the PV system would not be possible. PV inverters are therefore the link between the PV modules on your roof and firstly your personal electricity supply within your home and secondly the utility grid.
Types of solar inverters: models and versions
PV inverters are available in various versions for a variety of uses. Solar inverters are also available in different varieties, e.g. as solar inverter 10kw or solar inverter 6kw. The following inverters are those used most frequently:
Micro solar inverters / micro inverters
These micro inverters for solar panels are connected directly to the PV modules: you will find a PV inverter on every PV module. These inverters are often used for small PV systems, such as solar systems on balconies.
String inverters
With larger PV systems, the individual PV modules are connected one after another in a string formation. Rather than fitting a separate PV inverter for each module, this setup uses what are known as string inverters. These convert all the direct current (DC) produced by the group of modules into alternating current which can then be used and fed into the utility grid. A multi-string inverter combines the energy flow of several module strings and converts the energy produced from direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
Central inverters
Large ground-based PV systems, also known as PV farms, generally comprise hundreds of PV modules. Central inverters are used here to consolidate the strings of all modules and to convert the direct current (DC) that they produce into alternating current (AC). The central inverter is often located in a separate engineering room.
Battery inverters
Battery inverters are devices used in PV systems with a battery to convert the direct current (DC), which is stored by the batteries, into alternating current (AC). This conversion process allows the energy stored in the batteries to be made available for use in a home or to be fed into the utility grid.
Hybrid inverters
SMA hybrid inverters combine the functions of a PV inverter with those of a battery inverter in one device.
How do solar inverters work?
PV inverters have an important job to do in PV systems: the solar radiation strikes the PV modules, which convert the energy into direct current (DC). However this can be neither used in the home nor fed into the utility grid. So every PV system needs a PV inverter.
The direct current (DC) generated by the PV system is fed to the PV inverter via a cable.
The inverter converts the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
You can consume the alternating current straightaway in your own home or business or feed it into the local utility grid.
Additional functions of SMA PV inverters
In addition to this main function, an SMA PV inverter handles lots of other tasks too. The most important functions include the following:
![[Translate to English:] Ertrags- und Anlagenüberwachung](https://cdn.sma.de/fileadmin/content/website-meta/icons/svg/blue/50/monitor-heart-beat-circle-notification.svg?v=1645801872)
Yield and system monitoring
Monitoring of the PV system and checking the yields achieved don't have to be complicated tasks. SMA PV and solar inverters with a Home Management System can be controlled very easily via a smartphone or tablet. And you can view all the yield data conveniently and concisely in the Sunny Portal and SMA Energy App.
![[Translate to English:] Netzüberwachung](https://cdn.sma.de/fileadmin/content/website-meta/icons/svg/blue/50/oil-rig.svg?v=1654154605)
Grid monitoring
SMA PV inverters ensure that the voltage and frequency remain constant as the self-generated energy is fed into the household grid.
![[Translate to English:] Leistungsoptimierung](https://cdn.sma.de/fileadmin/content/website-meta/icons/svg/blue/50/chart-up-arrow-circle.svg?v=1645801871)
Power optimisation
SMA ShadeFix allows SMA PV inverters to always get the most out of PV modules – even if they are dirty or shaded. SMA ShadeFix uses MPP trackers to do this. MPP tracking stands for "Maximum Power Point Tracking". This means that SMA photovoltaic inverters adjust the electrical load in each PV cell and/or in each PV module such that each cell can supply the greatest amount of power possible.
![[Translate to English:] Sicherheit](https://cdn.sma.de/fileadmin/content/website-meta/icons/svg/blue/50/Shield__Protected-1.svg?v=1645801871)
Safety
Safety is a priority for SMA in the design and sale of its PV and solar inverters. Our concept for the safe operation of PV systems is based on various principles, which dovetail perfectly:
Lean PV systems with high-quality devices
Intelligent and innovative software functions
Extensive testing and quality inspections
40 years of global experience in PV technology development
Hands-on training for first-time PV owners and professionals
Difference between single-phase and three-phase inverters
There are single-phase and three-phase inverters on the market. The main differences between them are as follows:
Single-phase inverters
Single-phase PV inverters are connected to one power cable and/or line conductor. They are comparatively cheap and are suited to small PV systems.
Three-phase inverters
These inverters are connected to three power cables and/or three line conductors. They are more powerful, more energy efficient and more versatile.
At the start of 2012, the legislative authority in Germany passed a so-called code of practice (VDE-AR-N 4105) for ensuring maximum grid stability for the operation of PV systems. This legislation states that henceforth single-phase inverters may be used up to a system size with an apparent power of 4.6 kilovolt-amperes (kVA). If the apparent power of the PV system is greater than 4.6 kVA, then a three-phase inverter must be used. This is one of the reasons why three-phase inverters are now more frequently used in Germany.
The three-phase inverter is also becoming more common in Austria and Switzerland. The single-phase inverter is used for small PV systems but that tends to be the exception.
How do you choose a suitable PV inverter?
Choosing the right PV inverter as well as the right solar inverter sizes depends on a number of factors and is therefore usually best left to specialists. Here's an overview of the key steps:
First the maximum power output that the PV system can produce under ideal conditions is determined. Then a PV inverter that supports this level of direct current power is selected.
If surplus current is to be fed into the utility grid, a grid-tied PV inverter is needed. If however, there are no plans to feed into the grid, a PV inverter for stand-alone mode (off-grid) is suitable.
A decision is made as to whether the PV inverter should be a three-phase or single-phase variant.
Next, the efficiency of the models under consideration is compared. The more efficient the PV inverter, the higher the energy yield and the lower the losses.
The compatibility of the desired PV inverter with the installed or planned PV modules should also be checked.
And the installation site should be taken into account in the choice of PV inverter. Not all models are suited to all temperature ranges (e.g. the heat at the base of the roof in summer) or moisture levels (e.g. when installed outdoors).
Operating convenience and software features also play a major role in the selection. A PV inverter of SMA is intuitive to use and optimises the power output of PV systems by means of smart control.
Connecting inverters
The installation of a PV inverter should be planned well and the work should always be carried out by suitable professionals. When making the connection, note all the instructions in the valid operating manual for your device. The following points are particularly important:
Can solar inverters be installed outside? Ideally, the PV inverter is positioned in a dry, well-ventilated location, which is free of frost and protected from irradiation.
Locating it near the building's main electric circuit will reduce the amount of work involved and the cost of the connection.
Special PV cables must be used for the wiring. These can withstand the high electrical currents which the PV cells generate during high levels of irradiation.
Using as short a length of cable as possible with as wide a cross-section as possible ensures that the power of the modules can be fully utilised.
Frequently asked questions about PV / solar inverters
What kind of cable runs between the PV system and inverter?
Only certified cables of a suitable cross-section may be used between the PV system and PV inverter; these are resistant to abrasion and flames. The cable requirements are listed in the valid operating manuals for the respective inverter.
How powerful does the inverter for a PV system need to be?
The PV inverter must correspond to the PV system's maximum direct current power output. Devices that are larger aren't an issue but too low a performance is.
How long will an inverter last in a PV system?
Depending on the model, the PV inverters of SMA are designed for an operating period of roughly 25 years. Note regarding the cost of solar panel inverters: The solar inverters prices are an essential factor, especially when balanced against their expected lifespan and solar inverter efficiency or PV inverter efficiency.
How much current does a PV inverter consume?
The power consumption of a PV inverter depends on its power rating and model. During the day, the device draws its energy from the PV system. This means that electricity costs will only be incurred if it runs in idle mode during the night. But its power consumption is very low; our Sunny Tripower X, for example, uses less than 5 watts.
How many PV modules can be connected to an inverter?
The number of PV modules that can be connected to a solar or hybrid inverter depends on the power of the individual PV modules and the power class of the inverter.
For example: If the PV system consists of 10 modules with a power of 300 W each, that are connected in series, the maximum power is 3 kW peak. An inverter with a power of up to 3 kW should be used for such a system.
The PV system does not produce its full power for a majority of the time as the sun does not always shine evenly and the modules might be shaded. Even though SMA ShadeFix optimizes the power, full power cannot always be achieved so the system may be overdimensioned in comparison with the inverter. This means that an inverter with a power of 2 kW may be sufficient for a system with a peak output of 3 kW. An overdimensioned PV system is especially useful for hybrid inverters. This allows surplus power to be loaded straight into the battery without getting lost.
The optimum power class of the inverter depends on the specific characteristics of the PV system. PV installers can make more exact calculations using tools such as Sunny Design.
Can a PV system also run without an inverter?
In theory, you can connect up a PV system without any PV or solar inverters. This is standard practice for small module systems, e.g. for caravans. These transportable modules supply the on-board battery with direct current. If you were to run PV systems in your own home without an inverter, you would however have to switch your entire home over to consumers running on direct current (DC). This would require a huge amount of work.
What is the difference between inverters that feed into the grid and off-grid PV inverters ?
Off-grid inverters are not connected to the utility grid; the solar power generated on the roof is solely intended for self-consumption. PV and solar inverters which feed into the grid, on the other hand, feed any solar power which is not used into the utility grid. Owners of these kinds of systems receive a feed-in tariff for this power.